Home
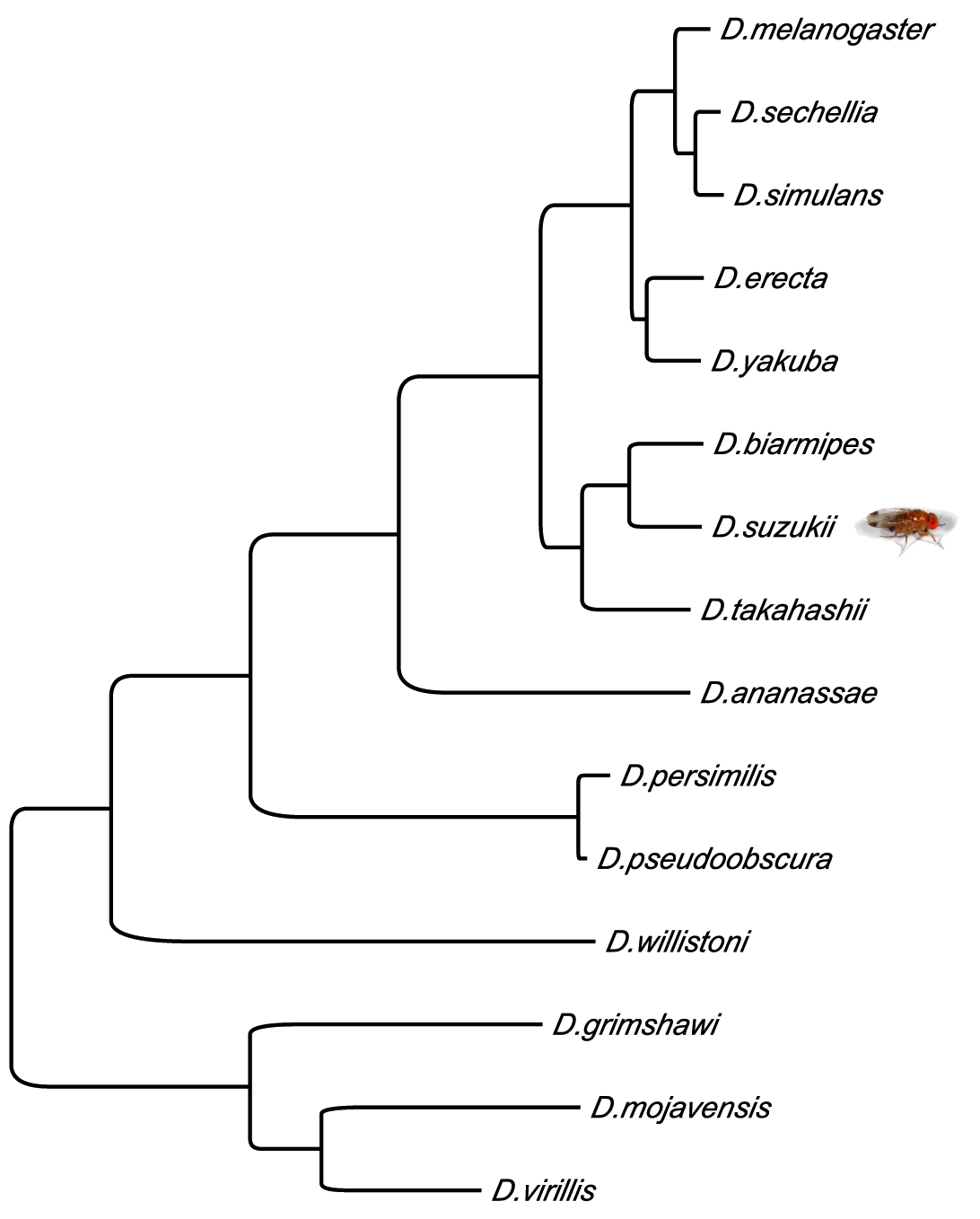
The SpottedWingFlyBase is a dedicated online resource for Drosophila suzukii genomics. The recently introduced and rapidly spreading Spotted Wing Drosophila (Drosophila suzukii) has unique anatomy among Drosophila species that enables it to become a serious economic pest. Female D. suzukii has a serrated ovipositor and exhibits a preference for ovipositing in sound ripe and ripening fruit as opposed to the overripe fruit that other Drosophila species are known to infest. Since its initial detection in the continental United States in 2008 in the berry-growing central coastal region of California, significant crop losses have been reported not only in California, but also throughout the United States, Canada, and Europe among growers of berry crops and soft-skinned stone fruits.
The goal of our database and web server is to provide comparative genomics resources to enable and streamline basic research on Drosophila suzukii biology as well as applied research to develop effective monitoring and control strategies for this invasive pest.
Publication
Chiu, J. C., X. Jiang, L. Zhao, C. A. Hamm, J. M. Cridland, P. Saelao, K. A. Hamby, E. K. Lee, R. S. Kwok, G. Zhang, F. G. Zalom, V. M. Walton, and D. J. Begun (2013). Genome of Drosophila suzukii, the Spotted Wing Drosophila. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics 3(12):2257-71. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.008185.
![]()
